GIT
GIT
Como usar o Git junto com outros colaboradores para controle de versão.
Ajuda do GIT:
[emerson@localhost TESTES]$ git --help usage: git [--version] [--exec-path[=GIT_EXEC_PATH]] [-p|--paginate|--no-pager] [--bare] [--git-dir=GIT_DIR]
[--work-tree=GIT_WORK_TREE] [--help] COMMAND [ARGS]
The most commonly used git commands are:
add - Add file contents to the index bisect - Find by binary search the change that introduced a bug branch - List, create, or delete branches checkout - Checkout a branch or paths to the working tree clone - Clone a repository into a new directory commit - Record changes to the repository diff - Show changes between commits, commit and working tree, etc fetch - Download objects and refs from another repository grep - Print lines matching a pattern init - Create an empty git repository or reinitialize an existing one log - Show commit logs merge - Join two or more development histories together mv - Move or rename a file, a directory, or a symlink pull - Fetch from and merge with another repository or a local branch push - Update remote refs along with associated objects rebase - Forward-port local commits to the updated upstream head reset - Reset current HEAD to the specified state rm - Remove files from the working tree and from the index show - Show various types of objects status - Show the working tree status tag - Create, list, delete or verify a tag object signed with GPG
See 'git help COMMAND' for more information on a specific command.
Considerações para este exemplo
Os exemplos são feitos em linha de comando do Linux. Site do GitHub: https://github.com/ Link do git usuário ‘surfx’: git@github.com:surfx Link do git colaborador ‘adolfont’: git@github.com:adolfont/TESTES.git:adolfont
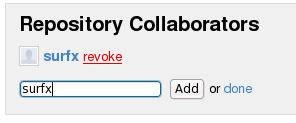
Obs: para que o usuário ‘surfx’ realizasse o push no branch git@github.com:adolfont/TESTES.git do colaborador ‘adolfont’, é necessário que o usuário ‘adolfont’ adicione o colaborador ‘surfx’ no branch git@github.com:adolfont/TESTES.git, conforme Figura 1.
Figura 1 – Colaboradores Git
Adicionado uma pasta para teste:
[emerson@localhost ~]$ cd Desktop/ [emerson@localhost Desktop]$ mkdir testegithub [emerson@localhost Desktop]$ cd testegithub/
“Clonando” dos dados do Git do colaborador ‘adolfont’:
[emerson@localhost testegithub]$ git clone git://github.com/adolfont/TESTES.git Initialized empty Git repository in /home/emerson/Desktop/testegithub/TESTES/.git/ remote: Counting objects: 18, done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (10/10), done. remote: Total 18 (delta 3), reused 0 (delta 0) Receiving objects: 100% (18/18), done. Resolving deltas: 100% (3/3), done. [emerson@localhost testegithub]$ cd TESTES/
Recupera o ramo atual:
[emerson@localhost TESTES]$ git branch * master
Lista os arquivos do diretório:
[emerson@localhost TESTES]$ ls README [emerson@localhost TESTES]$ cat README This file is here only for testing git. AQUI ESTÁ A ALTERAÇÃO CONFLITANTE.... Fazendo alteração conflitante. ##Gedit é um comando do Linux que permite editar um arquivo: [emerson@localhost TESTES]$ gedit README
Este comando do git adiciona novos arquivos:
[emerson@localhost TESTES]$ git add .
Commit dos dados na máquina local (-m ‘’ representa um comentário):
[emerson@localhost TESTES]$ git commit -a -m 'Testando alteração' [master 2f9be95] Testando alteração 2 files changed, 8 insertions(+), 0 deletions(-) create mode 100644 README~
Enviar os arquivos para o git do colaborador (git@github.com:adolfont/TESTES.git é o link do servidor GitHub do colaborador):
emerson@localhost TESTES]$ git push git@github.com:adolfont/TESTES.git master Counting objects: 5, done. Compressing objects: 100% (3/3), done. Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 353 bytes, done. Total 3 (delta 1), reused 0 (delta 0) To git@github.com:adolfont/TESTES.git 4253dde..2f9be95 master -> master
Comandos comuns do GIT
Para trocar de ramo:
[emerson@localhost TESTES]$ git checkout -b experimental Switched to a new branch 'experimental'
Listar os ramos existentes:
[emerson@localhost TESTES]$ git branch * experimental master
Para excluir um ramo:
[emerson@localhost TESTES]$ git branch -d experimental Deleted branch experimental (was 2f9be95).
Para criar um ramo:
[emerson@localhost TESTES]$ git branch master
Checkout em um ramo:
[emerson@localhost TESTES]$ git checkout master
Recuperar o log do GIT:
[emerson@localhost TESTES]$ git log
Listar os ramos existentes:
[emerson@localhost TESTES]$ git branch -r origin/HEAD origin/experimental origin/master
Recuperar o ramo no qual você esta:
[emerson@localhost TESTES]$ git branch * master
Checkout:
[emerson@localhost TESTES]$ git checkout master
Editar um arquivo:
[emerson@localhost TESTES]$ cat README
Editar um arquivo (linux):
[emerson@localhost TESTES]$ gedit README
Commit local (-m ‘comentário’):
[emerson@localhost TESTES]$ git commit -a -m 'ex de comentario - modificacao'
Add todos os novos arquivos:
[emerson@localhost TESTE_EMERSON]$ git add .
Inicializar GIT:
[emerson@localhost TESTES2]$ git init Initialized empty Git repository in /home/emerson/Desktop/testegithub/TESTES2/.git/
Adicionar no servidor (git@github.com:surfx/TESTES2.git é o link no servidor do GitHub):
[emerson@localhost TESTES2]$ git remote add origin git@github.com:surfx/TESTES2.git
Enviar os arquivos para o servidor:
[emerson@localhost TESTES2]$ git push origin master
Outra forma de se enviar os arquivos para o servidor (git@github.com:surfx/TESTES.git é o link no servidor do GitHub):
[emerson@localhost TESTES]$ git push git@github.com:surfx/TESTES.git master
Enviar os arquivos para o git do colaborador (git@github.com:adolfont/TESTES.git é o link do servidor GitHub do colaborador):
emerson@localhost TESTES]$ git push git@github.com:adolfont/TESTES.git master Counting objects: 5, done. Compressing objects: 100% (3/3), done. Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 353 bytes, done. Total 3 (delta 1), reused 0 (delta 0) To git@github.com:adolfont/TESTES.git 4253dde..2f9be95 master -> master
Tabela de conteúdo |
Para enviar um novo ramo para o GitHub
git push origin [novo-ramo-remoto]
Para baixar o ramo experimental do KEMS
1. Abrir um terminal.
2. Ir para uma pasta onde possa ser criado o diretório KEMS.
3. Baixar o KEMS:
git clone git://github.com/adolfont/KEMS.git
4. Ir para a pasta KEMS
cd KEMS
5. Baixar o ramo "experimental" com:
git branch --track experimental origin/experimental
6. Passar a usar o ramo "experimental"
git checkout experimental
Procedimento genérico para baixar e usar um ramo não-mestre de um projeto
git clone REPOSITORIO_GIT cd PASTA_PRINCIPAL git branch --track RAMO origin/RAMO git checkout RAMO
onde
- REPOSITORIO_GIT=local do repositório git
- PASTA_PRINCIPAL=pasta do projeto
- RAMO=ramo não-mestre do repositório
Para baixar atualizações
git pull git@github.com:adolfont/KEMS.git experimental