GIT
GIT
Como usar o Git junto com outros colaboradores para controle de versão.
Ajuda do GIT:
[emerson@localhost TESTES]$ git --help usage: git [--version] [--exec-path[=GIT_EXEC_PATH]] [-p|--paginate|--no-pager] [--bare] [--git-dir=GIT_DIR] [--work-tree=GIT_WORK_TREE] [--help] COMMAND [ARGS]
The most commonly used git commands are:
add Add file contents to the index bisect Find by binary search the change that introduced a bug branch List, create, or delete branches checkout Checkout a branch or paths to the working tree clone Clone a repository into a new directory commit Record changes to the repository diff Show changes between commits, commit and working tree, etc fetch Download objects and refs from another repository grep Print lines matching a pattern init Create an empty git repository or reinitialize an existing one log Show commit logs merge Join two or more development histories together mv Move or rename a file, a directory, or a symlink pull Fetch from and merge with another repository or a local branch push Update remote refs along with associated objects rebase Forward-port local commits to the updated upstream head reset Reset current HEAD to the specified state rm Remove files from the working tree and from the index show Show various types of objects status Show the working tree status tag Create, list, delete or verify a tag object signed with GPG
See 'git help COMMAND' for more information on a specific command.
Considerações para este exemplo
Os exemplos são feitos em linha de comando do Linux. Site do GitHub: https://github.com/ Link do git usuário ‘surfx’: [mailto:git@github.com git@github.com]:surfx Link do git colaborador ‘adolfont’: [mailto:git@github.com git@github.com]:adolfont
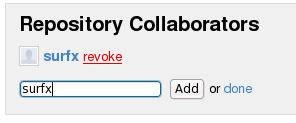
Obs: para que o usuário ‘surfx’ realizasse o push no branch git@github.com:adolfont/TESTES.git do colaborador ‘adolfont’, é necessário que o usuário ‘adolfont’ adicione o colaborador ‘surfx’ no branch [mailto:git@github.com git@github.com]:adolfont/TESTES.git, conforme Figura 1.
Figura 1 – Colaboradores Git
Adicionado uma pasta para teste:
[emerson@localhost ~]$ cd Desktop/ [emerson@localhost Desktop]$ mkdir testegithub [emerson@localhost Desktop]$ cd testegithub/
“Clonando” dos dados do Git do colaborador ‘adolfont’:
[emerson@localhost testegithub]$ git clone git://github.com/adolfont/TESTES.git Initialized empty Git repository in /home/emerson/Desktop/testegithub/TESTES/.git/ remote: Counting objects: 18, done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (10/10), done. remote: Total 18 (delta 3), reused 0 (delta 0) Receiving objects: 100% (18/18), done. Resolving deltas: 100% (3/3), done. [emerson@localhost testegithub]$ cd TESTES/
Recupera o ramo atual:
[emerson@localhost TESTES]$ git branch * master
Lista os arquivos do diretório:
[emerson@localhost TESTES]$ ls README [emerson@localhost TESTES]$ cat README This file is here only for testing git. AQUI ESTÁ A ALTERAÇÃO CONFLITANTE.... Fazendo alteração conflitante. Gedit é um comando do Linux que permite editar um arquivo: [emerson@localhost TESTES]$ gedit README
Este comando do git adidciona novos arquivos:
[emerson@localhost TESTES]$ git add .
Commit dos dados na máquina local (-m ‘’ representa um comentário):
[emerson@localhost TESTES]$ git commit -a -m 'Testando alteração' [master 2f9be95] Testando alteração 2 files changed, 8 insertions(+), 0 deletions(-) create mode 100644 README~
Enviar os arquivos para o git do colaborador ([mailto:git@github.com git@github.com]:adolfont/TESTES.git é o link do servidor GitHub do colaborador):
emerson@localhost TESTES]$ git push git@github.com:adolfont/TESTES.git master Counting objects: 5, done. Compressing objects: 100% (3/3), done. Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 353 bytes, done. Total 3 (delta 1), reused 0 (delta 0) To git@github.com:adolfont/TESTES.git 4253dde..2f9be95 master -> master
Comandos comuns do GIT
Para trocar de ramo:
[emerson@localhost TESTES]$ git checkout -b experimental Switched to a new branch 'experimental'
Listar os ramos existentes:
[emerson@localhost TESTES]$ git branch * experimental master
Para excluir um ramo:
[emerson@localhost TESTES]$ git branch -d experimental Deleted branch experimental (was 2f9be95).
Para criar um ramo:
[emerson@localhost TESTES]$ git branch master
Checkout em um ramo:
[emerson@localhost TESTES]$ git checkout master
Recuperar o log do GIT:
[emerson@localhost TESTES]$ git log
Listar os ramos existentes:
[emerson@localhost TESTES]$ git branch -r origin/HEAD origin/experimental origin/master
Recuperar o ramo no qual você esta:
[emerson@localhost TESTES]$ git branch * master
Checkout:
[emerson@localhost TESTES]$ git checkout master
Editar um arquivo:
[emerson@localhost TESTES]$ cat README
Editar um arquivo (linux):
[emerson@localhost TESTES]$ gedit README
Commit local (-m ‘comentário’):
[emerson@localhost TESTES]$ git commit -a -m 'ex de comentario - modificacao'
Add todos os novos arquivos:
[emerson@localhost TESTE_EMERSON]$ git add .
Inicializar GIT:
[emerson@localhost TESTES2]$ git init Initialized empty Git repository in /home/emerson/Desktop/testegithub/TESTES2/.git/
Adicionar no servidor ([mailto:git@github.com git@github.com]:surfx/TESTES2.git é o link no servidor do GitHub):
[emerson@localhost TESTES2]$ git remote add origin [mailto:git@github.com git@github.com]:surfx/TESTES2.git
Enviar os arquivos para o servidor:
[emerson@localhost TESTES2]$ git push origin master
Outra forma de se enviar os arquivos para o servidor ([mailto:git@github.com git@github.com]:surfx/TESTES.git é o link no servidor do GitHub):
[emerson@localhost TESTES]$ git push git@github.com:surfx/TESTES.git master
Enviar os arquivos para o git do colaborador ([mailto:git@github.com git@github.com]:adolfont/TESTES.git é o link do servidor GitHub do colaborador):
emerson@localhost TESTES]$ git push git@github.com:adolfont/TESTES.git master Counting objects: 5, done. Compressing objects: 100% (3/3), done. Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 353 bytes, done. Total 3 (delta 1), reused 0 (delta 0) To git@github.com:adolfont/TESTES.git 4253dde..2f9be95 master -> master